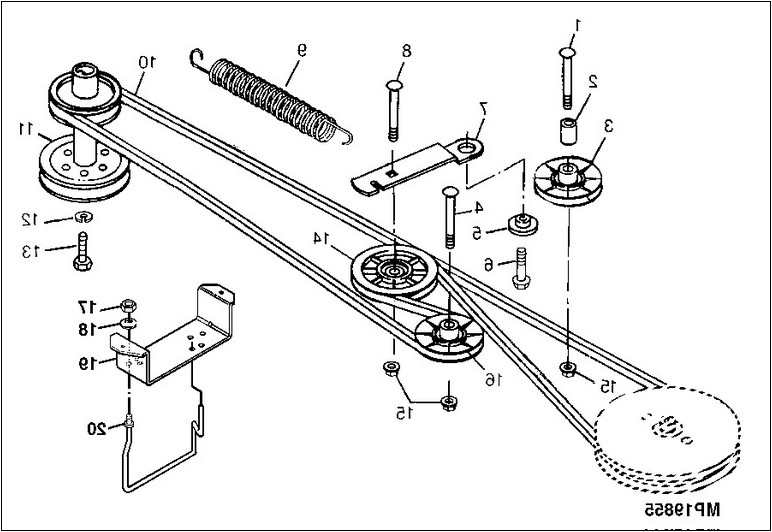
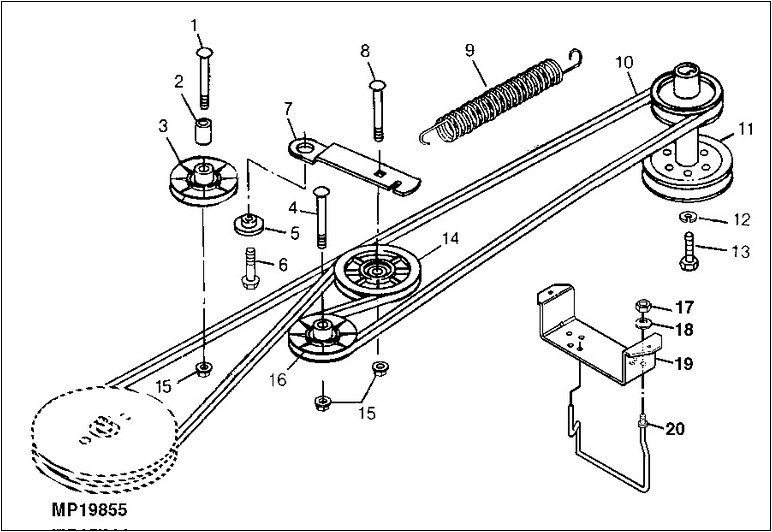
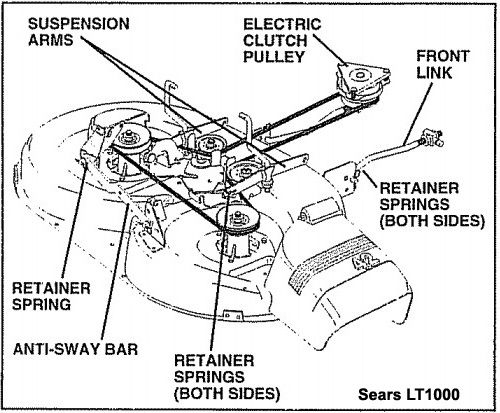
42 Inch Craftsman Riding Mower Drive Belt Diagram – Belt diagrams provide a visual representation of the layout and routings of belts in various mechanical systems. They offer visual representations of how belts are placed around various components, aiding engineers, mechanics, and DIY enthusiasts working on HVAC systems, or other belt-driven machines.
Types and applications of Belt Diagrams
- Serpentine belt diagrams will be employed when a single continuous belt is driving several devices.
- Timing belt diagrams illustrate the location and alignment of a timing chain which connects the crankshaft with camshaft(s), in order to ensure the proper timing of valves.
- V-belt diagrams show the placement of multiple V-shaped belts on older engines or special systems, each of which drives each component.
The most important components of Belt Diagrams
- Pulleys, also known as circular devices with belts that loop around them, transfer power from one area to the next.
- Belts, the elastic bands that transmit the power between pulleys are referred to as
- Tensioners maintain correct tension on the belt, to avoid slippage and guarantee smooth operation.
How to Read a Belt Diagram
- Understanding symbols helps you identify components and routing patterns in the schematic.
- Identifying key components such belts, pulleysand tensioners and belts lets you see the layout of the system.
- Understanding routing patterns lets you to see how the belt moves, and how it affects different parts.
This is a step-by- step guide to making a Belt Diagram:
- Collect important data: Accurately measure, specify and arrange the components, belt(s) and their arrangement
- Sketch the initial layout. Sketch out a blueprint that shows the layout of the entire system. It also shows the position of each pulley and tensioner.
- Add Tensioners and Pulleys. Label each pulley with its component (e.g. power steering pump or alternator).
- Draw the Belt Routing Diagram Draw the course of the belt(s) around pulleys, following industry standards or specifications from the manufacturer to ensure the proper routing.
- Revise and improve your diagram: Check all of your work to ensure accuracy. making any changes necessary to create a clear, simple diagram.
Tips for Belt Diagrams
- With the right software tools, making attractive and professional-looking diagrams is simpler, faster and cost-effective.
- For creating a precise and practical belt diagram, it is important to get accurate information from the specifications of the manufacturer, service manuals or other trustworthy online sources.
- Checking the diagram twice for mistakes before you submit it to the editor ensures accuracy and reliability. This can eliminate any confusion that may arise during repairs or maintenance.
Conclusion
The ability and understanding to draw belt diagrams is crucial for anyone who works with belt-driven machines. Knowing the difference between diagrams, the way they are constructed, and how to effectively construct them will make you more equipped to tackle any job that requires pulleys or belts. These tricks and tips will help you create concise and precise diagrams that are more efficient and productive.